It has never been easier to learn about digital advertising than now, with all the resources available on the web. One of the biggest hurdles newcomers meet is quite simple — where to start? Find out in the text below.
Where to start?
As you can imagine, digital advertising covers a wide variety of disciplines, approaches, and types. Before you immerse yourself in advanced Performance marketing subjects and read about Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO), Inbound Marketing, or programmatic, you should familiarize yourself with some Digital Advertising basics.
Understanding the difference between impressions and reach, how digital advertising can benefit you, and how to craft a digital advertising strategy will give you enough knowledge to continue your learning journey about Digital Advertising.
As I said, you should start from the basics, which certainly includes defining what Digital Advertising is.
What is Digital Advertising?
Webster’s dictionary (everyone references it in the movies, so why not me) defines advertising as “the action of calling something to the attention of the public, especially by paid announcements”. Plainly, we can describe advertising as paying to communicate a specific message to your customers or users. Adding Digital means that you use various digital channels for that process.

Search Advertising
Search advertising, also known as Paid Search, is a type of advertising where advertisers use search engines to serve ads to users while actively searching for a solution to their problems. That makes Search Advertising one of the most effective types of advertising because it’s based on explicit user needs.
Display Advertising
Display advertising is the type of advertising that uses image ads served to users through many different websites. It’s perfect for reaching a wide variety of users thus building your brand awareness.
Video Advertising
Video advertising can be defined similarly to Display advertising, but instead of images, advertisers use video content for their ads.
Native Advertising
With Native advertising, advertisers use paid content that looks like organic content to the user. The most straightforward example of Native advertising would be a paid news article — to the average user, it will look and feel like any other article. Still, the copy will try to influence their behavior just like any other ad would.
Social Media Advertising
Some might consider Social Media advertising a combination of Display, Video and Native advertising. The main feature is serving ads through different Social Media platforms, and most often, they are hardly distinguishable from organic content users see on those platforms.
Email Advertising
Email advertising is the type of advertising where users receive promotional messages to their email addresses. This means that advertisers often know who will see and read their message, making it ideal for message personalization. That being said, it also means that advertisers should ask for explicit consent to receive promotional emails from their target audience.
Of course, there are many more types of Digital Advertising, depending on how you define differentiating factors, but you could consider these the most prominently used. Who knows, we might even write about those other types in the future, so check out our blog from time to time.
Another frequently asked question concerning Digital Advertising is — Why should I advertise on digital channels?
There are multiple advantages of Digital Advertising, so let’s see how digital advertising can benefit you.

Benefits of Digital Advertising
-
Precise targeting and personalization
You have greater and more precise targeting options when advertising on digital channels. You can define which age group you want to target, what interests they have, their online and offline behavior, and much more.
With such precise targeting, there are also great personalization possibilities, meaning that you can craft your messages for a niche audience and serve your ads only to them.
On the other hand, to enhance user privacy, there have been some changes in privacy and cookie policies that will limit targeting options, but more on that in future blog posts, so stay tuned.
-
Easy to measure and optimize
Imagine this scenario: you are advertising in traditional media (print, radio, TV), and you notice an uptake in your revenue, so you know your advertising is paying off, right?
But why and how exactly?
You don’t know which specific ad and channel are most responsible. You also don’t know who exactly sees your ad and how they react to it.
With Digital Advertising, it’s much different because you can have all that information which will give you much more relevant data, making it easier to focus your campaign optimization efforts.
Just like with targeting options, changes in privacy and cookie policies will limit the data available to advertisers, but that just means we’ll have to find a way to adapt. It’ll be fun to watch how everyone leverages those changes to their benefit.
-
It’s Affordable & Scalable
Digital Advertising sounds interesting, but it must be costly, right? Not really — you can start with a minimal budget, much smaller than almost any other advertising channel.
What’s even better is the possibility to easily scale your advertising. Because you are getting real-time reporting for your advertising efforts, you can see which parts of your campaigns perform better and slowly allocate more budget toward them.
-
That’s where your customers are
Gone are the days when it was enough to advertise in print media, radio, or TV. This is evident just by looking at the distribution of advertising spending worldwide in 2021.
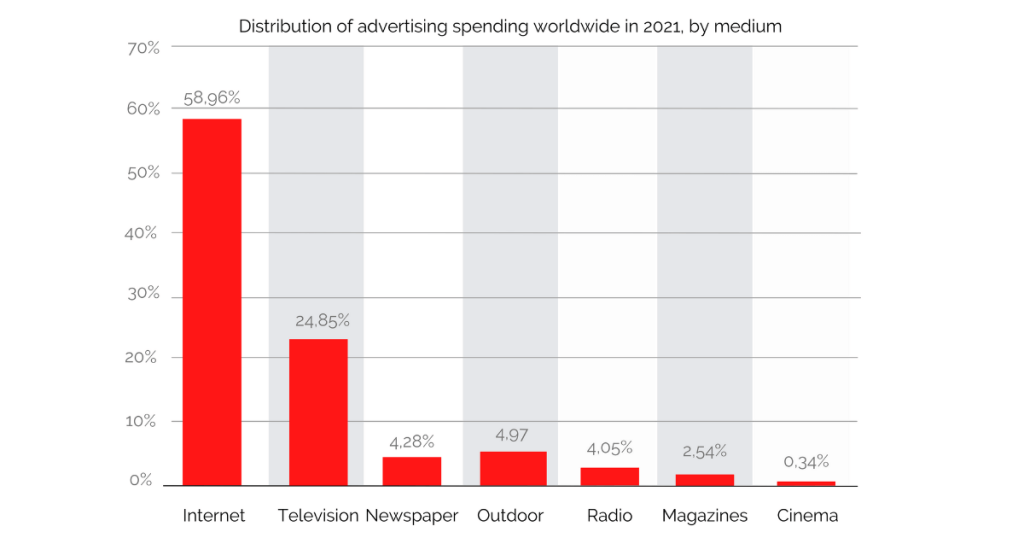 As you can see, advertisers are switching to digital advertising because they know that they’ll have an easier time reaching their target audience (amongst other reasons listed above).
As you can see, advertisers are switching to digital advertising because they know that they’ll have an easier time reaching their target audience (amongst other reasons listed above).
If you’re not advertising on digital, be sure that your competitors most certainly are.
We should also talk about the main Digital Advertising metrics used to monitor campaign results. They are relatively easy to understand, but there are some specifics you should be aware of.
Digital Advertising Metrics
Reach and Impressions
Impressions show how many times your ad was shown to a user, while reach shows how many different users have seen your ad. Although they might seem similar, there is a very important difference that I noticed many people don’t quite understand.
Let’s try an example: you and four of your friends are walking around the city and all five of you saw a giant billboard. This means that this billboard had 5 impressions. Next, 2 of your friends had to go somewhere, and the rest continued walking around the city and saw another giant billboard. So how many impressions were achieved by both billboards together? Well, 8, of course, 5 for the first one, and only 3 for the second one. But how many people have both billboards reached together? They reached only 5 people because there were five of you in total.
From this simple example, you can see why it would be wrong to calculate the total reach of your campaign by adding reach from each ad you are using in that campaign. One individual user could have seen any number of your ads.
Clicks
Clicks show the number of times users clicked on your ad. That means that your ad is linked to some website you wish your target audience to visit most of the time. An important thing to note — a click doesn’t necessarily mean that the user visited your website. They might have closed the browser before the website loads, so you can’t monitor your website traffic using the Clicks metric.
Click-Through Rate
Click-Through Rate (CTR) shows the percentage of times people saw your ad and clicked on it.
Conversions
Conversion could be anything. Conversions occur when someone completes the desired goal, with you defining what that goal is. If you manage an e-commerce website, the main conversion you would be looking for is a purchase. If you want people to subscribe to your newsletter, you can define subscription as a goal.
Engagement
Engagement shows the number of interactions your ad received. Those interactions could be any number of things — clicks, video views, likes, shares, etc.
Cost Per x
Campaign results depend on many different factors, with your campaign budget being one of them. Since you can’t compare the results of a campaign that had a budget of €100 and another campaign that had a budget of €1000, you’ll have to use average prices to see which performed better.
Those prices could be Cost per Click (CPC), Cost per Conversion (more frequently referred to as Cost per Acquisition or CPA), Cost per Engagement, etc.
ROAS
You probably heard about Return on Investment (ROI) which measures the profitability of your investment. ROAS is just that, but it only takes Advertising Spending into account. It is a better metric to use if you want to evaluate your campaign’s efficiency by seeing how much you are earning for every Euro spent (or any other currency you are using).
Sessions and Users
A session is a period when a user is actively engaged with your website, so looking at this metric will give you an insight into how much traffic your website receives. The user is someone who has initiated at least one session on your website.
Bounce rate
The bounce rate shows you the percentage of users who left your website without interacting with it.
These are not all the metrics you’ll use to monitor your campaigns, but they are enough to start.
Ok, that’s all fine and dandy, but where should you start?

How to start with digital advertising?
Now that you have familiarised yourself with the basics and are thinking about leveraging Digital Advertising to your advantage, you might ask yourself what’s the best approach for implementing a Digital Advertising campaign. Before doing anything else, you should start crafting a Digital Advertising strategy.
But what does that mean? You might ask yourself. Firstly, you should know your goal, what you want to achieve with your advertising campaign, whether you want to build awareness, generate traffic to your website, sell your products, etc.
Without a goal in mind, everything else would be meaningless, and you would just be throwing your money away.
Next, you should consider your target audience, their interests, how they use the internet, do they just scroll casually through their news feeds, or are they actively searching for something?
When you define your goal and target audience, start thinking about which advertising channel is best suited for reaching your target audience and achieving your goal. For instance, if you want to generate brand awareness, you’ll probably use some combination of Social Media and Display advertising.
On the other hand, if you want to sell your products to users while they are searching for them, then, of course, you’ll use Search advertising.
After deciding on an advertising channel, defining and structuring your ad messaging would be the next thing in line. What messaging triggers or UVPs would work best? Which call-to-action should you use? Should messaging differ for a user who is just searching for some information and a user who is searching for a solution?
All these decisions about what, how, to whom, etc., form a Digital Advertising strategy. Still, as you can see from this brief introduction, there are many things to consider if you want to create a perfect digital advertising strategy.
So what do you think? Did I manage to demystify Digital Advertising at least a bit for you?
This was just a little taste of everything Digital Advertising has to offer, so browse our blog for more information if you are interested in the subject.
And if you are interested in working with us, be sure to contact us.



